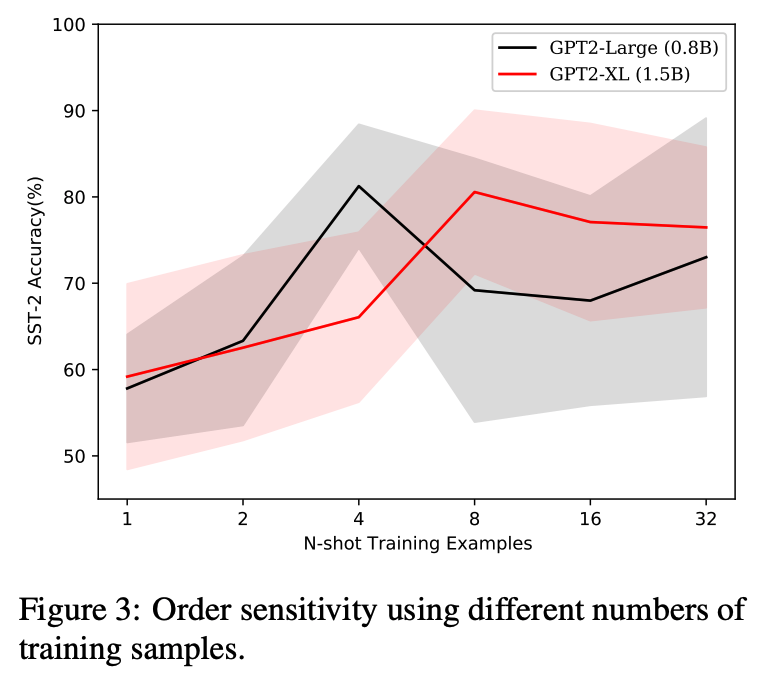
When primed with only a handful of training samples, very large pretrained language models such as GPT-3, have shown competitive results when compared to fully-supervised fine-tuned large pretrained language models. We demonstrate that the order in which the samples are provided can be the difference between near state-of-the-art and random guess performance: Essentially some permutations are “fantastic” and some not.
We analyse this phenomenon in detail, establishing that: it is present across model sizes (even for the largest current models), it is not related to a specific subset of samples, and that a given good permutation for one model is not transferable to another. While one could use a development set to determine which permutations are performant, this would deviate from the few-shot setting as it requires additional annotated data. Instead, we use the generative nature of the language models to construct an artificial development set and based on entropy statistics of the candidate permutations from this set we identify performant prompts.
Our method improves upon GPT-family models by on average 13% relative across eleven different established text classification tasks.

Twitter
Facebook
Reddit
LinkedIn
Google+
StumbleUpon
Pinterest
Email